(Ⅳ) Chemical Safety
Chemical Safety
(Ⅰ)Purchase of Chemicals
1.A series of assessment has to be carried out by relevant departments inclu- ding safety office, prior to the purchase of hazardous chemicals that are hi- ghly toxic or are ingredients for making toxins or explosives. Upon approval, the Hazardous Articles Warehouse of the University Resources Center should be responsible for the purchase.
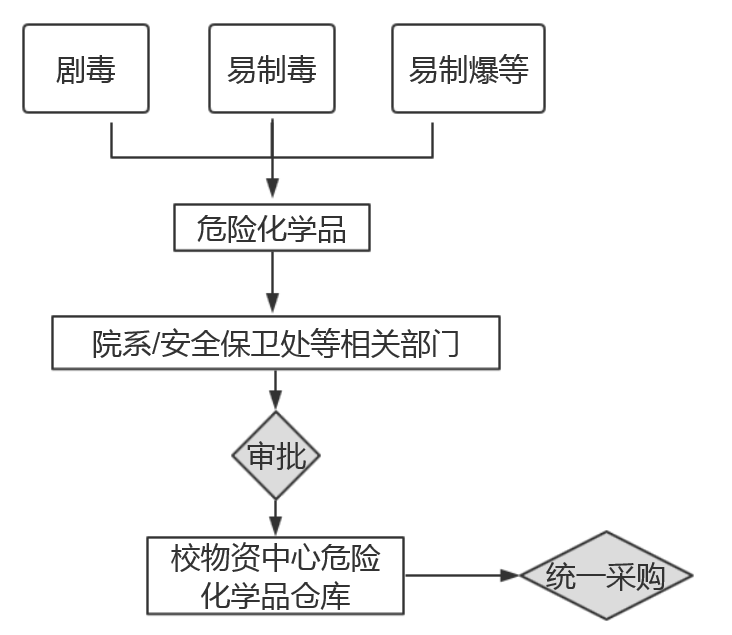
(Ⅰ)Purchase of Chemicals
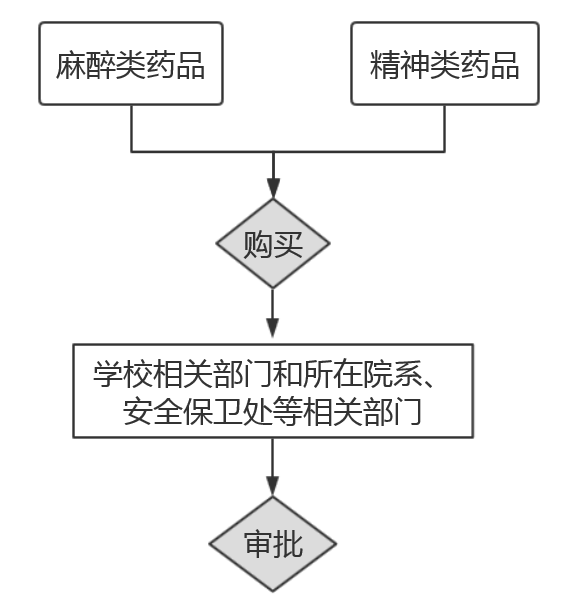
2.The purchase of narcotic or psychiatric drugs has to be approved by releva- nt school authorities as well as governmental departments.
Chemical Safety
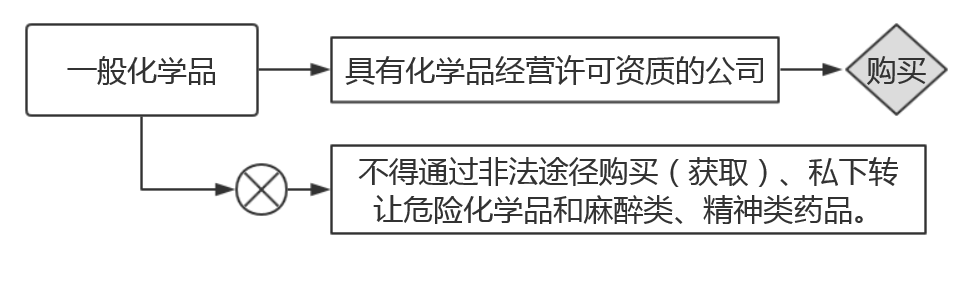
(Ⅰ)Purchase of Chemicals
3.Common chemicals should be purchased from companies with chemical business licenses or permission.
4.Do not purchase illegally, obtain or sell unofficially hazardous chemicals, narcotic drugs or psychiatric drugs.
Chemical Safety

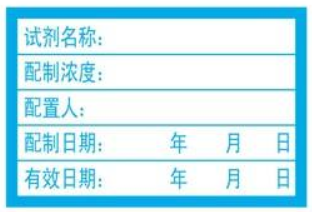
(Ⅱ)Preservation of Chemicals
1. General Guidelines
1.1All chemicals and reagent have to be tagged with identifiable labels. Do not tag labels with partial information or next to an existing one. Include the in- formation such as name, concentration or purity, person responsible, date of the reagent or reaction product.
Chemical Safety

Chemical Safety
(Ⅱ)Preservation of Chemicals
1. General Guidelines
1.2The places storing the chemicals should be clean, well ventilated, safety with good insulation and away from heat or fire.

Chemical Safety
(Ⅱ)Preservation of Chemicals
1. General Guidelines
1.3 Do not store large quantity of reagent especially in barrels in the laborato- ry. Do not store large amount of flammable materials, explosives or strong oxidants in the laboratory. Chemicals should be stored in tightly sealedco- ntainers and categorized. Do not store together chemicals that are incom- patible or can produce strong reaction.
Chemical Safety
(Ⅱ)Preservation of Chemicals
1. General Guidelines
1.4Keep a day-to-day inventory of the chemicals. Dispose waste chemicals timely.

Chemical Safety
(Ⅱ)Preservation of Chemicals
2.Requirements for Storing and Categorizing Dangerous Chemicals
2.1Highly toxic chemicals, narcotic drugs and psychiatric drugs should be sto- red in a safe or fridge with double lock. The request, transport, usage and lock of those chemicals should be conducted by at least two persons simu- ltaneously. Keep relevant records in time.


Chemical Safety
(Ⅱ)Preservation of Chemicals
2.Requirements for Storing and Categorizing Dangerous Chemicals
2.2Explosives should be stored separately from flammables or oxidants un- der 20 centigrade. Better to be stored in an explosion-proof reagent cabi- net or fridge.

Chemical Safety
(Ⅱ)Preservation of Chemicals
2.Requirements for Storing and Categorizing Dangerous Chemicals
2.3Corrosive chemicals should be placed on the lower shelf of the anti-corr- osion reagent cabinet or in an anti-corrosion tray in an ordinary reagent cabinet.
2.4Reducing agent and organic substance should not be stored together with oxidants, sulfuric acid or nitric acid.
Chemical Safety
(Ⅱ)Preservation of Chemicals
2.Requirements for Storing and Categorizing Dangerous Chemicals
2.5Strong acid, especially sulfuric acid, should not be stored together with st- rong oxidant salts like potassium permanganate and potassium chlorate. Do not mix salts like potassium cyanide, sodium sulphide, sodium nitrite, sodium chlorate and sodium sulfite with acids as they might create toxic gases.


Chemical Safety
(Ⅱ)Preservation of Chemicals
2.Requirements for Storing and Categorizing Dangerous Chemicals
2.6Place chemicals that can create toxic gas or fume in a ventilated reagent cabinet.
2.7Alkali metal like sodium or potassium should be stored in kerosene, wher- eas yellow phosphorus and mercury should be stored in water.
Chemical Safety
(Ⅱ)Preservation of Chemicals
2.Requirements for Storing and Categorizing Dangerous Chemicals
2.8Do not mix medicines like acetic anhydride, acetyl chloride and thionyl ch- loride that are likely to hydrolyze with aqueous solution, acid or alkali.
2.9Do not store halogen (fluorine, chlorine, bromine and iodine) with ammon- ia, acid and organics.
2.10Do not mix ammonia with halogen, mercury, hypochlorous acid and acid.

Chemical Safety
(Ⅲ)Usage of chemicals
1. Read Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) before experiments. Learn about the properties of various chemicals and take proper protective measures.
Chemical Safety
(Ⅲ)Usage of chemicals
2.Follow the lab instructions strictly for achieving the objective of experiments. Try to reduce the usage of dangerous substances or replace them with low- risk substances.
3.Maintain good ventilation in the workplace. When using chemicals, do not directly touch, taste or smell the chemicals.
Chemical Safety
(Ⅲ)Usage of chemicals
4.Do not heat organic solvent in an open container or a close container using open flame. Do not store dry flammable organics in an oven.

Chemical Safety
(Ⅲ)Usage of chemicals
5. Lab personnel should wear goggles, lab coats with long sleeves, trousers,socks and other protective equipment. (Comment: Cotton lab coats are not recommended for handling flammable materials!)
6.When using alkali metal (potassium, sodium and so forth), do not mix it with water or aqueous solution.
Chemical Safety
(Ⅳ)Disposal of Chemical Waste
1.Clean up chemical waste after experiments. Store together those with the similar chemical properties. Use the original bottle or a narrow-mouth con- tainer with threaded cap to store the chemical waste in different categories, labeled with “For Chemical Waste Only”, except for those empty bottles. (A- ll the labels can be purchased in the Hazardous Articles Warehouse of the University Resources Center) Make sure all the containers are sealed clo- sely without leakage. Flasks storing waste fluids should be placed in a blue plastic container with compartments for separating items inside. 10 liters special barrel storing chemical waste fluids should not be overfilled (no more than the max line marked on the barrel)
Chemical Safety
(Ⅳ)Disposal of Chemical Waste
2.Store organic waste fluids containing halogen, inorganic waste fluids cont- aining mercury, arsenic or heavy metal separately. Do not mix them with others.
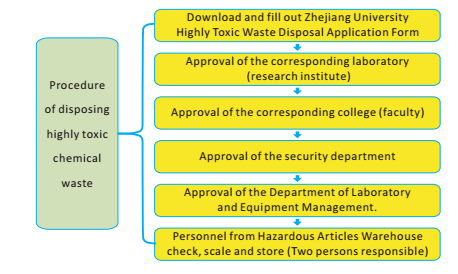
3.Chemicals that are radioactive, explosive (there are 8 types of explosives,including detonating devices and detonating agent, nitro aromatic explos- ives, nitrate explosives, nitroglycerin composite explosives, chlorate composite explosives, perchlorate composite explosive, liquid oxygen expl- osive and black powder), contagious, polychlorinated biphenyl or dioxin should be disposed first to change their chemical property before trans- ported to the chemical waste pickup point in the campus.
Chemical Safety
(Ⅳ)Disposal of Chemical Waste
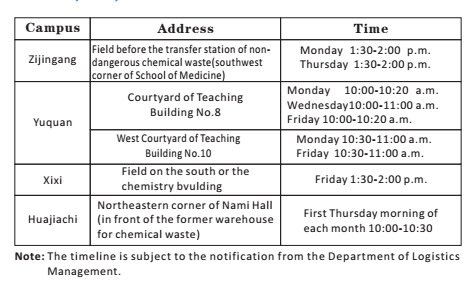
4.The personnel responsible for storing and transporting hazardous was- tes should take Zhejiang University Laboratory Chemical Waste Regis- tration Form (with 3 copies; available on the website of the Department of Logistics Management). Transport chemical waste to the waste acc- umulation areas of the campuses according to the given schedule. As- sist the staff on site with their work.

Chemical Safety

Chemical Safety
(Ⅳ)Disposal of Chemical Waste
5.Do not dispose highly toxic waste together with normal chemical waste. Fill out the Zhejiang University Highly Toxic Waste Disposal Application Form (available from the website of the department of laborary and equipment m- anagement). After approval from relevant departments, store them temporarily in the school dangerous chemical storage.
6.Collect or adsorb and decompose toxic gas before release.
Chemical Safety
(Ⅴ)First Aid
Inform the supervisor once chemical incidents take place. Perform first aid procedures and then take the injured to hospital for medical treatment.
1.Chemicals Burns
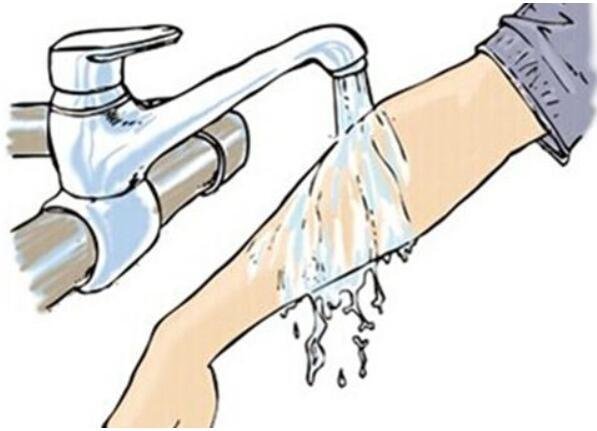
Take off clothes conta minated with chemicals. Wash with a large amount of water for a long period to avoid enl- arging the burned area. If the burned area is relatively small, wash with cold water for about 30 minutes and then-

Chemical Safety
(Ⅴ)First Aid
1.Chemicals Burns
-apply ointment for burns. If the burned area is large, apply clean fabric (or ga- uze, towel, sheet) soaked with cold water onto the wound. Get medical attent- ion immediately. When managing the wound, try to maintain the integrity of the skin with blister. Do not tear off the wounded skin. Do not apply colored medi- cine or other substances (like mercurochrome, gentian violet, soy sauce or to- othpaste). Otherwise it will affect the judgment on the depth of the wound and treatment.
Chemical Safety
(Ⅴ)First Aid
2.Chemical Erosion
Remove contaminated clothing immediately. Wash the wound with a large amount of water or appropriate solvent or solution. Keep the wound clean for further medical treatment. If chemical contacts the eyes, immediately wash the eyes with thin strain of water. If only one eye is affected, protect the unaff- ected eye from water used to wash other eye.

Chemical Safety
(Ⅴ)First Aid
3.Chemical Frostbite
Move the wounded away from the low temperature environment and freez- ing objects. Use warm water about 40 degrees centigrade to defrost the clot- hes, and then take them off or cut them off. Warm the affected area. Seek me- dical attention immediately. For people experiencing cardiac respiratory arre- st, perform cardiac compression and resuscitation. Do not parch, apply an ice pack to the affected area, soak the affected area in cold water, or punch on the affected area.
Chemical Safety
(Ⅴ)First Aid
4. Inhalation of Toxic Chemical
4.1 Cut off the source of poison immediately (e.g. turn off the valve of the pump,plug the equipment leaking). Open windows and doors to reduce the con- centration of poison.
4.2 Before entering the area having poisonous gases, please wear protective respirator and clothing.
4.3 Move the exposed person to fresh air soon. Perform first aid accordingly. Dial 120 for medical help.

Chemical Safety
(Ⅴ)First Aid
5. Swallowing Chemicals by Mistake
5.1 Swallowing Ordinary Chemicals
To reduce the concentration of chemicals in the stomach, slow down the rate of absorption and protect gastric mucosa, immediately drink milk or water or eat egg, flour, starch or mashed potatoes. Otherwise drink water with activ- ated carbon (normally every 10-15 grams can absorb about 1 gram of toxin) to provoke vomiting or excreting. Seek medical attention immediately.
Chemical Safety
(Ⅴ)First Aid
5. Swallowing Chemicals by Mistake
5.2 Swallowing Strong Acid
Immediately drink 200ml 0.17% calcium hydroxide solution, 200ml magn- esium oxide suspension, 60ml 3-4% aluminum hydroxide gel, milk, vegetable oil or water to dilute toxins. Eat 10 more dissolved eggs as alleviator. Seek me- dical attention immediately. Do not arbitrarily induce vomit or perform gastric lavage as first aid measures.

Chemical Safety
(Ⅴ)First Aid
5. Swallowing Chemicals by Mistake
5.3 Swallowing Strong Alkali
Immediately drink 500ml diluted vinegar solution (1 portion of vinegar for 4 portions of water) or diluted fresh tangerine juice, then take olive oil, egg white, milk and etc. Seek medical attention immediately. Do not arbitrarily induce vo- mit or perform gastric lavage as first aid measures.

Chemical Safety
(Ⅴ)First Aid
5. Swallowing Chemicals by Mistake
5.4 Swallowing Pesticide
For organic chloride poisoning, immediately induce vomit or perform gas- tric lavage. Use 1-5% sodium bicarbonate solution or warm water to pump the stomach, and then use 60ml 50% magnesium sulfate solution. Forbid using oil laxative. Seek medical attention immediately.
For organophosphate pesticide poisoning, use sodium bicarbonate solu- tion to pump the stomach; for those swallow dip Terex, use saline or water to pump the stomach. Forbid using sodium bicarbonate solution. Meanwhile, Se-
ek medical attention immediately.

Chemical Safety
(Ⅴ)First Aid
6.Gas Explosion
Immediately cut off the power and gas. Evacuate personnel, move other explosive materials away. Notify the fire department.